Automatic Vegetation Classification is part of the Classification tool within the  Automatic Point Cloud Analysis tool.
Automatic Point Cloud Analysis tool.
![]() This tool requires Global Mapper Pro.
This tool requires Global Mapper Pro.
The Vegetation Classification tool detects and classifies high vegetation points in point cloud data, such as trees and large shrubs. There are two algorithms for ground classification. Choose one of these options from the drop down window:
-
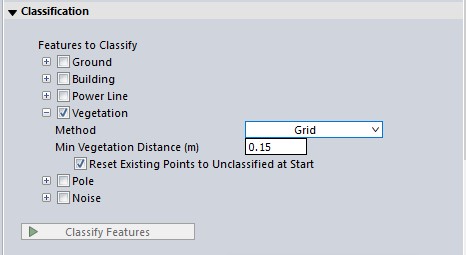
Grid is the traditional method and was designed for aerial, fixed wing collected lidar. It classifies points based on their geometric relationship to a best fit plane. This is the method best for aerial lidar with multiple returns in forested areas.
-
Max Likelihood uses segmentation, and is developed to work with more modern point clouds such as terrestrial lidar, programmatic, and drone-mounted. The Segmentation Method segments the point cloud into clusters of points, and then determines if those clusters are likely building or vegetation points. Similar parameters, with more detailed options, appear in the stand-alone Segmentation tool.
You can choose to run multiple classifications at once by checking multiple options (noise, ground, etc). They will run in a pre-specified order based on method.
Once your settings have been determined for all desired classifications, click Classify Features to begin processing.
Note: Prior to using the vegetation classification tool, the point cloud should have ground classified. If the ground is not classified, check the box to run ground classification as well. The Automatic Point Cloud Analysis tool will classify ground (and noise if selected) before vegetation.
Classification and Extraction Shared Settings:
The two vegetation classification algorithms share multiple settings with the Feature Extraction tool:
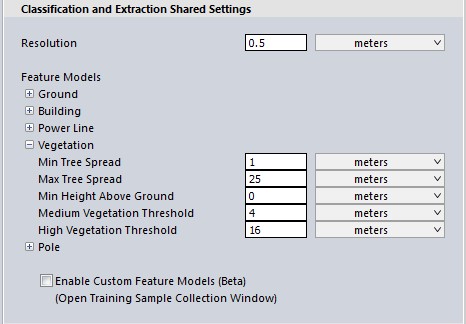
Minimum Tree Spread
The minimum width (edge-to-edge) of a single tree canopy.
Maximum Tree Spread
Specify the maximum tree spread (canopy width expected per tree) in meters. These settings help to distinguish clusters of tree into individuals.
Minimum Height above ground
Use this setting to specify the minimum height above ground for a tree. . This helps to distinguish bushes from trees.
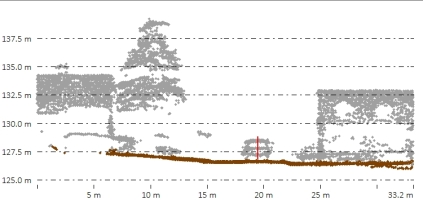
The default value is 3 meters. Typically, buildings and high vegetation points are at least 2 meters above the ground, as in the example below. This value can help eliminate other objects, such as cars, from the classification.
The red line in the above path profile views illustrates the 2 meter height above ground, in comparison to a car. All points below the height above ground value will be removed from consideration as buildings or trees.
Medium/ High Vegetation Thresholds
When using Max Likelihood classification and Feature Extraction, these are minimum height values used to distinguish Medium and High vegetation.
Vegetation Classification Settings
The Max Likelihood Method
The classification of vegetation points involves a statistical analysis (Principal Component Analysis) of clusters of nearby points to determine what is likely part of a tree feature. Points are gathered into clusters based on a measure of similarity between nearby points, with the intent to group points that belong to the same object or feature.
Once neighborhoods are established and quantified using Principal Component Analysis, a measure of point-to-point similarity is evaluated to guide clustering. This similarity measure is evaluated as a generalized statistical distance between points, based on the distributions defined by the statistics collected over their local neighborhoods. Clustering aims to group points with similar surface characteristics into groups that can be classified based on those characteristics.
-
The settings in the Geometric Segmentation tool can be used in Max Likelihood classifications. Simply open the Geometric Segmentation tool, choose your settings, and check the box to Use Custom Segmentation Parameters. These settings will influence how the point cloud is segmented.
-
To train the algorithm for your specific feature, check the box to enable Custom Feature Models. These settings will influence how the point cloud is classified.
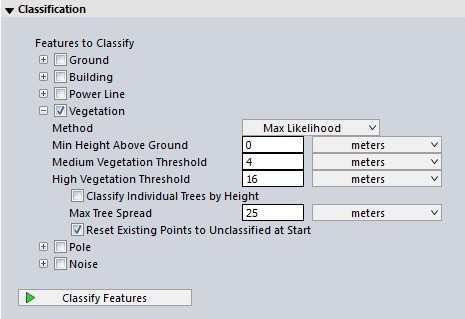
Classify Individual Trees by Height
Check this option to divide classified vegetation points into low, medium, and high vegetation. The thresholds that determines these are found in the shared settings, in the left side of the Point Cloud Analysis tool.
Note about resolution for segmentation (Max Likelihood) methods:
The principal component analysis, part of the segmentation process, is used to evaluate characteristics of the surface to which a point belongs. That analysis includes other points in a local neighborhood and evaluates average properties that quantify the surface at a point.
Neighborhood Range (determined by resolution) defines the region around a point that will be evaluated to determine local surface properties; it should roughly be on the same scale as the features being evaluated. For example, when trying to characterize building roof planes, this value should be large enough that the included points clearly define a surface plane. Point density influences the choice of this parameter; a good value will define neighborhoods with enough points to define reliable statistics. Using the resolution option for this parameter is a good way to guarantee that neighborhoods include a sufficient number of points.
Changing the resolution will have the largest impact on the classification results.
With a lower density point cloud, such as moderate resolution aerial lidar, the neighborhood range should be similar to the size of the major parts of the building, such as a plane of a roof, often around 3-4 point spacings.
With a high density point cloud, such as terrestrial lidar in which it is possible to visually detect parts of buildings (like windows, smaller roof planes or chimneys), the neighborhood range should be roughly at the scale of those smaller components--sometimes as small as 0.2 - 0.4 meters.
The Grid Method
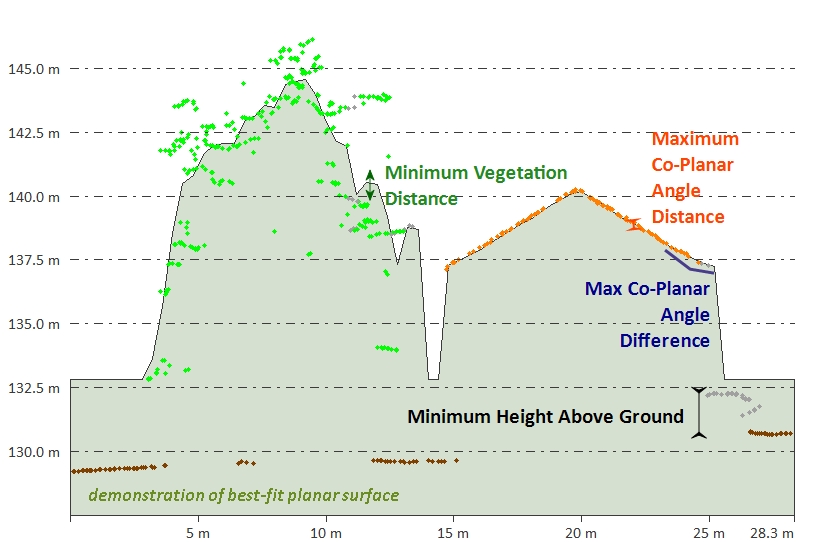
The Gridded Method is best designed for use with aerial lidar. This method works similarly to the Grid method found in Building Classification: it classifies points as "building" or "tree" based on their relationship to a calculated best-fit planar surface inside each segment (bin) of points. Points that are close to the calculated plane are classified as building, and points that are far from the planar surface are classified as high vegetation.
Minimum Vegetation Distance
Use this field to set the maximum distance (in meters) that the points in a small region all have to be within, in order to consider the region a potential vegetative region. As shown below, this is similar to the auto-classification of building points.
Reset Existing Points to Unclassified at Start
Resets the Unclassified Non-Ground Point data, resetting any points classified as non-ground. Removes all manual and automatic classification of ground points in selected point data, setting all points to unclassified.