Automatic Noise Classification
Noise Classification is part of the Classification tool found within the  Automatic Point Cloud Analysis tool.
Automatic Point Cloud Analysis tool.
![]() This tool requires Global Mapper Pro.
This tool requires Global Mapper Pro.
Noise Classification automatically detects and can remove likely noise points from point cloud data. Noise points are outliers generated during collection or processing that can have an adverse influence on analysis. Classify noise points first to avoid them being classified incorrectly in another analysis.
There are two methods for noise classification: Grid and Max Likelihood. Choose one of these options from the drop down window:
-
Grid is the traditional method and was designed for aerial, fixed-wing collected lidar. This was the standard method in earlier versions of Global Mapper. When this option is enabled simultaneity with ground classification, the noise classification will be performed first.
-
Max Likelihood uses segmentation, and is developed to work with more modern point clouds such as terrestrial lidar, programmatic, and drone-mounted.
When the classification has finished, a pop-up window will display the number of points classified as low noise and high noise.
You can choose to run multiple classifications at once by checking multiple options (noise, ground, etc). They will run in a pre-specified order based on method.
Once your settings have been determined for all desired classifications, click Classify Features to begin processing.
Automatic Noise Classification
The Grid Method
This method is based on the same algorithm as Ground Grid MCC classification. 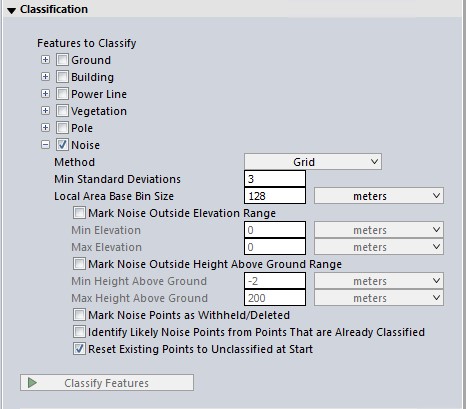
Minimum Standard Deviations
Specify the minimum allowed variance from the local average of height values for the loaded or selected points in standard deviations. Points more than the specified number of standard deviations away from a local average height will be identified as noise. The default value is 3 standard deviations.
Local Area Base Bin Size
Specify the sample spacing at which to detect noise. The specified local area is used in a 5x5 neighborhood to determine outliers of the specified standard deviation. In most cases this bin size should be a larger value than some of the other bin size settings, in order to correctly account for expected variance in the data. The default value is 128 sample spacings. So with the default values, if the cloud resolution is about 0.1 meters per pixel, the local group would be a 5x5 set of sample cells (12.8 meters on each side).
Additional options for limiting which points are considered:
Mark Noise Outside Elevation Range - Manually define an elevation range, outside of which points will be defined as noise. The default values will be the minimum and maximum elevations for the loaded data.
Mark Noise Outside Height Above Ground Range - Manually define a height above ground range, outside of which points will be defined as noise. It is recommended to use this setting only if the point cloud had existing ground classifications. If there is no ground classification, the height above ground values will be very approximate, and may be inaccurate.
Mark Noise Points as Withheld/ Deleted - Check this option to delete the resulting classified noise points from the workspace. This has the benefit of ensuring that noise points will be omitted from all future point cloud processing, but at the risk of removing the ability to visually QC the classification. Tip: use the Render Deleted Features function (Ctrl + Shift + D) to visualize the deleted points in the workspace.
Identify Likely Noise Points from Points that are Already Classified - This will also consider points that have existing classifications as possible noise points.
Reset Existing Noise Point to Unclassified at Start - Resets existing noise points to unclassified.
The Max Likelihood Method
The Max Likelihood option uses segmentation to identify and classify likely noise points from the point cloud.
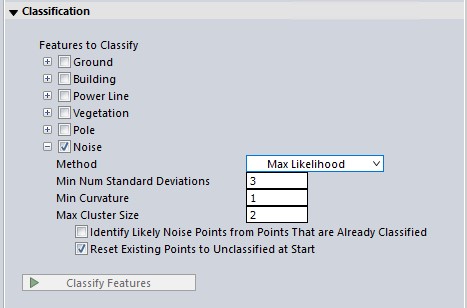
Minimum Standard Deviations
Specify the minimum allowed variance from the local average of height values for the loaded or selected points in standard deviations. Points more than the specified number of standard deviations away from a local average height will be identified as noise. The default value is 3 standard deviations. If this parameter is too small, then little or no clustering will happen and there will be a low probability of detection. If this parameter is too large, then clustering may be overly permissive and there will be a high probability of false alarm.
Min Curvature
Specify minimum curvature (in degrees) to help define non-noise points. The Max Likelihood algorithm classifies points as noise when they do not belong to a segment. The curvature value helps to determine the segmentation of non-noise points. Smaller values will result in more points classified as noise, as it restricts the definition of non-noise as points which belong to a reasonably flat surface.
Max Cluster Size
Clusters with more points than this threshold will not be classified as noise. Useful for excluding objects in sparse point clouds.
Restore Defaults
Resets the numeric parameters on the dialog to default values.