Color/ Contrast Adjustment
The Color/Contrast Adjustment tab (pictured below) allows you to control the color balance and contrast of the selected overlay(s).
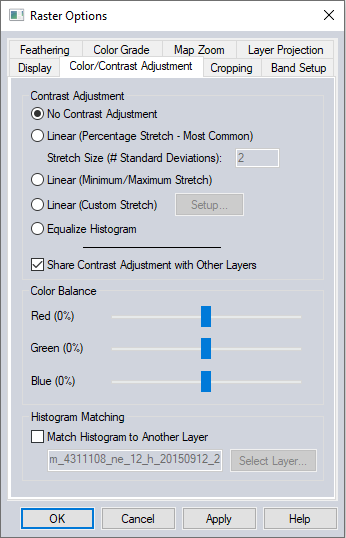
Contrast Adjustment
The Contrast Adjustment options are used to adjust the contrast of imagery. Most raw photographic imagery data requires some contrast adjustment to optimize the visible contrast between the most frequent data values. The data values within the image need to be represented in the RGB colorspace of the monitor, which contains values from 0-255 (one byte for each of the color bands).
No Contrast Adjustment
This option directly colors pixels on screen based on the data values. With no contrast adjustment, 8-bit values (0 to 255) are mapped directly into the RGB colorspace. 16-bit values (0-65535) are divided by 256 to get a range from 0-255.
Linear (Percentage Stretch)
This contrast adjustment method applies a standard deviation contrast adjustment to each color channel in the image. It optimizes the visible color range to show contrast for the majority of the data. Any outlying values beyond the specified standard deviation will be assigned the lowest or highest color value (0 or 255). The default of 2 standard deviations is generally recommended.
This setting is particularly useful for improving the display of dark or satellite imagery. Dark water or highly reflective urban and bare earth surfaces that have outlying values are grouped into the lowest or highest values, therefore allowing more color contrast for pixels closer to the average reflectance such as fields, forest, etc.Linear (Minimum/ Maximum Stretch)
This method automatically finds the minimum and maximum values in each color channel and stretches that range to a range of 0 to 255. For most imagery with 8-bits or less per color channel this will have little effect, but can produce a good result for high-color imagery.
Linear (Custom Stretch)
This method allows you to set the specific stretch range for each band of an image. The set range of values will then be stretched to the range of 0 to 255. Click Setup... after selecting this method to view a histogram for each band, and set the custom stretch range. Select each band from the Band dropdown and enter the lower and upper limits for the stretch range. Any bands that you do not specify a custom range for will stretch to the full min/max range of values in that band, as if the the Linear (Minimum / Maximum) stretch option was used for that band.
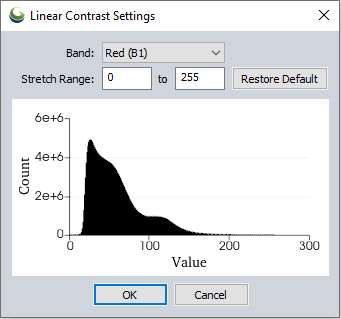
The Linear Contrast Settings dialog can be made larger by adjusting the edges. Scroll with the mouse wheel to zoom in on the histogram. Hover the cursor over the histogram data to see the value and count.
Equalize Histogram
This method more uniformly distributes the values in each color channel, stretching them to the full range of 0 to 255 and remapping them based on the original value and value frequency. Histogram equalization is used to improve the contrast in low-contrast images.
Share Contrast Adjustment with Other Layers
This check box allows the user to specify that the calculated contrast adjustment used should be based on all loaded raster layers that have contrast adjustment enabled, rather than the color histogram, for this single layer. This is enabled by default and provides consistent results when adjusting the contrast for multiple mosaiced images.
Color Balance
The Color Balance sliders allow you to modify the relative amounts of red, green, and blue in the image, thus allowing precise control over the color balance in the image.
Histogram Matching
Histogram Matching uses the color channel histograms from another image layer loaded in the Global Mapper workspace to manipulate the values in the original image to align with the distribution of values in the reference image. This method of image adjustment is useful for balancing the contrast and color for a set of images (tiles) collected at different dates/times.
Histogram Matching can only be done on layers with the same band data type (i.e. unsigned 16-bit, unsigned 8-bit, etc.) and only works on layers with 16-bit or smaller samples. You cannot use the Equalize Histogram contrast adjustment mode and Histogram Matching on the same layer at the same time.
Check the box for Histogram Matching, and when prompted select the image layer to use as the reference. The Select Layer... button can be used to change the selected reference layer.