Shapefile
Load Shapefile
A shapefile stores non-topological geometry and attribute information for the spatial features in a data set. The geometry for a feature is stored as a shape comprising a set of vector coordinates. Additional files represent the attributes, coordinate system information, metadata, etc. To load a shapefile point to the *.shp file. Global Mapper supports loading Shapefiles directly from .tar.gz files, so you do not need to uncompress your Shapefile data if you do not want to.
If the shapefile contains a metadata *.shp.xml, this information can be viewed with Metadata in an Additional tab.
Export Shapefile
The Export Shapefile command allows the user to export any loaded vector data sets to ESRI Shapefile format files.
When selected, the command displays the Shapefile Export Options dialog (pictured below) which allows the user to set up the export. The dialog consists of a File Selection, an Attribute Setup, Tiling, and an Export Bounds tabs which allows the user to set up the portion of the loaded vector data they wish to export.
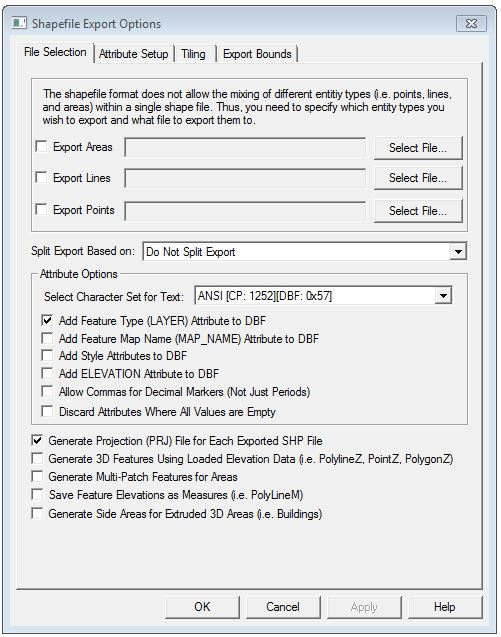
The Export Areas,
Export Lines, and Export Points
options enable area, line, and point export respectively. Pressing the
Select... button next to each
of those options allows you to select the name of the SHP file to generate.
In addition to the SHP file containing the actual geometry of the features,
an shape index file (SHX) and attribute database file (DBF) will be created
as well with the same name as the SHP file.
The Attribute Options allow for additional control over when and how attributes are exported to the shapefile. Select Character Set for Text supports the display of text in a character set other than the current system character set. When this is checked the text from a DBF file is not converted from the character set stored in the DBF file to the system active character set, but is kept native.
In general, Global Mapper will automatically determine an appropriate field type and length for any attributes exported to the DBF file created along with a Shapefile based on the values of the attribute data being exported. However, if your input data includes Shapefiles or DBF files, the original field type and length for an attribute will be used unless the attribute values being exported make that impossible.
The Split Export Based On option splits
up the export into separate files based on the feature type/classification,
feature description, feature name, or any attribute found in the loaded
data.
Choose the Split on Feature Type
option, to get the export split based on the feature classification, except
in the case of the unknown types, in which case the feature description
will be used automatically. The type/description/name/attribute value
of the features stored in each file will be appended on to the end of
the selected filenames.
The Discard Attributes When All Values are Empty option will discard any attributes on export if all values for the attribute in the features being exported to the file are blank
If selected, the Generate Projection (PRJ) File option causes a projection file describing the ground reference system of the shapefile to be generated for each shapefile created. The PRJ files will have the same name as the SHP file with the .prj extension.
If selected, the Add Feature Type (LAYER) Attribute to DBF option specifies that the type description for each exported feature will be added as a LAYER attribute to the DBF file generated with the SHP file.
If selected, the Add Style Attributes to DBF option specifies that style attributes should be added to the generated DBF file containing information about the drawing style and label font used for each feature. If you check this then when you reload your data in Global Mapper (but typically not other applications) it should maintain its drawing style.
If selected, the Generate 3D Features Using Loaded Elevation Data option specifies that 3D objects should be created in the shapefile. The elevation stored for each vertex/point will be the first of the following which is available:
- The elevation associated with the vertex/point in question.
- The elevation associated with the entire feature being exported. For example, the elevation of a contour line.
- The first elevation obtained by searching the loaded elevation grid layers at the position of the vertex/point.
- A
value of 0.0 will be used if no elevation could be obtained via any
of the prior methods.
If selected, the Generate Multi-Patch Features for Areas option specifies that multi-patch features should be generated for area exports rather than normal polygon records. This is useful for exporting 3D models, such as those you would load from Google SketchUp SKP files.
If selected,
the Save Feature Elevations as Measures
option specifies that Measure features (i.e. PolyLineM, PointM) should
be created. The per-vertex elevations will be stored as the Measure values.
Typically you might use this if your per-vertex elevations are actually
something like shotpoint numbers and not really elevations.
Use Generate Side Areas for Extruded
3D Areas to generate a 3D area feature with the extrusion mode.
When exporting a 3D Shapefile with this checked. additional areas
for the sides and bottom of the 3D area are created, similar to a 3D box
for a building.
The Attribute Setup tab will contain
a list of the default Attributes that will be exported to the dataset,
and contain the following information on the Attributes in a grid:
- Name - the name of the attribute as stored in Global Mapper
- Export Name - the name of the attribute as it will appear in the exported file
- Type - the data type for the attribute
- Length - the length of the data
- Precision
- number of digits right of the decimal for floating point data
The contents of the Type, Length, and Precision
columns can be changed by clicking on the grid cell. The Name
and Export Name columns are read-only.
When the user clicks on a cell in the Type
column, a drop-down list containing the supported data types will be displayed.
The user can select one of the types from the list.
When the
user clicks on a cell in the Length
or Precision column, the column
can be edited in place, allowing the user to type a new value directly
into the cell. If the user types a lower value into the Length or
Precision column, GM will display a warning indicating that that action
may cause a loss of data. A Precision value can only be entered if the
Type is 'Float'.
The tab also
contains a button that will remove the selected column(s) from the export.
Note that the grid contains all of the attributes
on the layers that are available for export. If the user chooses
to export a subset of the data (e.g., only area features), then
only the attributes associated with the designated features will be exported.
Any changes made in the grid will be applied when the attributes
are exported.
WARNING: The Shapefile format uses a DBF file for attribute storage, which means that any attribute names are limited to 10 characters. Any attribute names longer than that will be truncated with a number potentially added on to maintain uniqueness among multiple long attribute names.
Format Updates
Below is a summary of recent changes to shapefile format support: